In the IT landscape, ETL (extract, transform, load) processes have long been used for building data warehouses and enabling reporting systems. Using business intelligence (BI) oriented ETL processes, businesses extract data from highly distributed sources, transform it through manipulation, parsing, and formatting, and load it into staging databases. From this staging area data, summarizations, and analytical processes then populate data warehouses and data marts.
Most certainly, ETL tools have their place in the IT environment, as numerous database admins utilize ETL tools to facilitate process and deliver optimal value to business.
- Data Warehousing: Historically, the primary use for ETL tools has been to enable business intelligence. Pulling databases, application data and reference data into data warehouses provide businesses with visibility into their operations over time and enable management to make better decisions.
- Data Integration: Data integration allows companies to migrate, transform, and consolidate information quickly and efficiently between systems of all kinds. ETL tools reduce the pain of manually entering data and allow dissimilar systems to communicate, all the while supplying a unified view.
ETL Tools Get Complicated
ETL tools indeed provide a method of communication between databases and applications, but pose significant challenges over time. Because creating this type of connectivity requires an comprehensive knowledge of each operational database or application, interconnectivity can get complicated as it calls for implementing very invasive custom integrations.
Over time, this approach grows increasingly complex, and the greater the number of interconnected systems, the more complicated things become. Moreover, with such tight coupling, interdependencies create the potential for big, unpredictable impacts when even the slightest changes are made. The custom point-to-point data-level integrations become a tangled web of brittle connections, quickly beginning to look like “spaghetti code”.
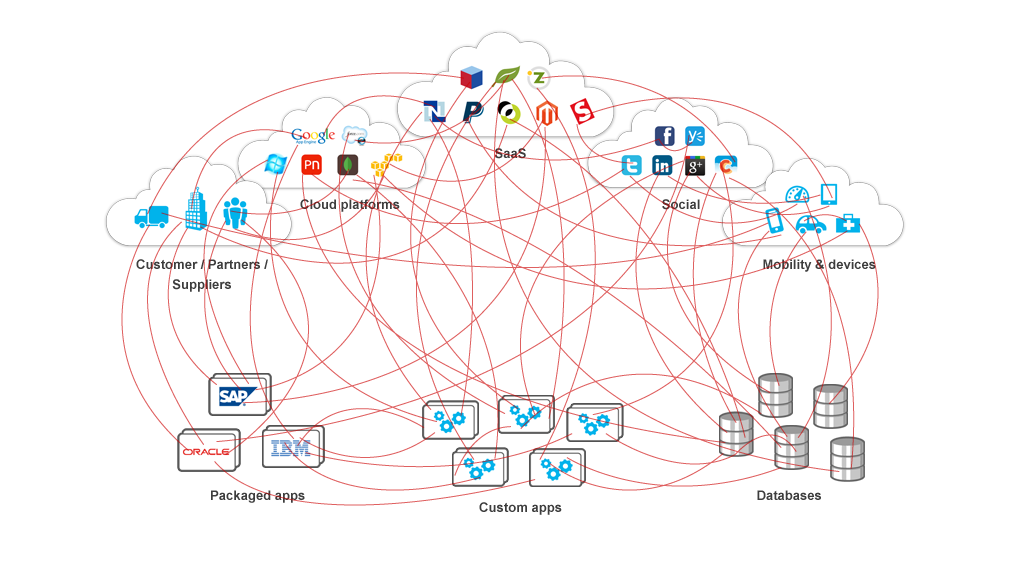
APIs and ESBs Simplify Data Integration
The increase in popularity of APIs has also made it much easier to create connectivity. With APIs, developers can access endpoints and build connections without having in-depth knowledge of the system itself, simplifying processes tremendously. As ETL tools remained focused more towards BI and big data solutions, and as traditional operational data integration methods become outdated with the rise in popularity of cloud computing, ESBs become better options to create connectivity.
An enterprise service bus (ESB) provides API-based connectivity with real-time integration. Unlike traditional ETL tools used for data integration, an ESB isolates applications and databases from one another by providing a middle service layer. This abstraction layer reduces dependencies by decoupling systems and provides flexibility. Developers can utilize pre-built connectors to easily create integrations without extensive knowledge of specific application and database internals, and can very quickly makes changes without fear of the entire integrated system falling apart. Shielded by APIs, applications and databases can be modified and upgraded without unexpected consequences. In comparison to utilizing ETL tools for operational integration, an ESB provides a much more logical and well defined approach to take on such an initiative.
Some of the commonly used ESBs in the Software Industry
1. Oracle Service Bus (OSB)
2. Mule ESB
3. Fuse ESB
4. Talend ESB
Nice article.
ReplyDeleteI was not knowing you are into blog stuff.
Thanks Jinay!
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete• Nice and good article. It is very useful for me to learn and understand easily. Thanks for sharing your valuable information and time. Please keep updating. Power Bi Online Training Bangalore
ReplyDelete